Allergies in Children A Comprehensive Guide
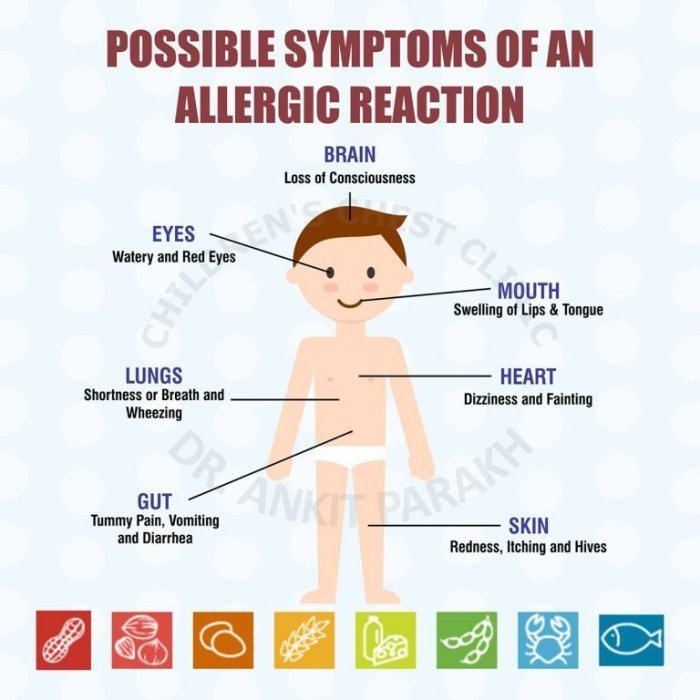
Allergies in children represent a significant concern for parents and healthcare providers alike. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of childhood allergies, exploring common types, diagnostic methods, effective management strategies, and the crucial impact on a child’s development, both physically and emotionally. We’ll examine the anxieties faced by families, offering practical coping mechanisms and resources to navigate these challenges effectively.
From understanding the prevalence of various allergies across different age groups to learning about the latest allergy testing procedures and treatment options, this comprehensive overview aims to equip readers with the knowledge and tools necessary to support children living with allergies. We will also address the often-overlooked mental health aspects associated with managing childhood allergies, providing guidance on stress reduction, anxiety management, and fostering resilience within the family unit.
Stress and Anxiety Management Techniques
Living with allergies can be stressful for children, impacting their daily routines and emotional well-being. Effective stress and anxiety management techniques are crucial for helping children cope with the challenges associated with their allergies and improve their overall quality of life. These techniques empower children to develop resilience and self-regulation skills, leading to better emotional health and improved allergy management.
Mindfulness Practices for Children with Allergies
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can significantly benefit children with allergies. These techniques help children focus on the present moment, reducing anxiety related to potential allergic reactions or triggers. Regular mindfulness practice can cultivate a sense of calm and self-awareness, enabling children to better manage their emotional responses to allergy-related stressors. For example, a child anticipating a trip to a park (a potential pollen trigger) might use deep breathing exercises to calm their anxiety before going.
This proactive approach helps them manage their fears and enjoy the experience.
Positive Self-Talk and Affirmations
Positive self-talk and affirmations are powerful tools for managing anxiety. By replacing negative thoughts with positive and encouraging statements, children can build self-confidence and resilience. For instance, instead of thinking “I’m going to have a bad reaction,” a child can affirm, “I can manage my allergies, and I’m safe.” Repeating positive affirmations regularly helps to reprogram the mind and fosters a more optimistic outlook, reducing the overall impact of allergy-related stress.
Consistent use of positive self-talk can help children feel more empowered and in control of their condition.
Breathing Exercises for Children
Teaching children simple breathing exercises is an effective way to manage anxiety in the moment. These techniques help regulate the nervous system and promote relaxation.
Here is a simple guide with examples:
- Belly Breathing (Diaphragmatic Breathing): Lie down or sit comfortably. Place one hand on your chest and the other on your belly. Breathe in slowly through your nose, feeling your belly rise. Hold for a few seconds, then exhale slowly through your mouth, feeling your belly fall. Repeat several times.
Imagine blowing up a balloon with each inhale and letting the air out slowly with each exhale.
- Balloon Breath: Inhale deeply, filling your lungs with air like a balloon. Hold the breath for a few seconds, then slowly exhale, making a “whoosh” sound like air escaping from a balloon. Repeat this several times.
- Lion’s Breath: Sit comfortably with your legs crossed. Inhale deeply through your nose, then open your mouth wide and exhale forcefully, sticking out your tongue and making a “haaa” sound. Repeat several times. This exercise can be particularly helpful in releasing tension.
Depression Support Resources for Families
Living with a child’s allergies can be incredibly stressful, and this stress can sometimes contribute to depression in parents and caregivers. It’s crucial to remember that seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness, and there are many resources available to provide support and guidance during challenging times. This section Artikels several avenues for families navigating the emotional toll of managing childhood allergies.Families facing depression related to managing allergies often benefit from a multifaceted approach to support.
This includes connecting with others facing similar challenges, accessing professional mental health services, and utilizing online and community-based resources. Remember that you are not alone in this journey.
Support Groups and Online Communities, Allergies in children
Connecting with other families who understand the unique challenges of managing childhood allergies and the associated emotional burdens can provide invaluable support. Sharing experiences, offering advice, and simply knowing you’re not alone can significantly ease feelings of isolation and overwhelm. Many local hospitals and allergy clinics offer support groups specifically for parents of children with allergies. Online forums and social media groups dedicated to allergy management also offer a space for connection and shared experiences.
These communities provide a platform to ask questions, share coping strategies, and find encouragement from others who understand. A search for “allergy parent support group” or similar terms online will reveal many options.
Seeking Professional Help for Depression
While support groups and online communities offer valuable peer support, professional help is crucial for managing depression effectively. A therapist or counselor can provide a safe and confidential space to explore feelings, develop coping mechanisms, and receive personalized treatment. Many mental health professionals specialize in helping families cope with the stress of chronic illness management. A family doctor or pediatrician can provide referrals to therapists or psychiatrists, who can then assess the situation and recommend appropriate treatment, such as therapy or medication.
Early intervention is key to managing depression effectively and improving overall well-being.
Relevant Organizations and Contact Information
Several organizations offer resources and support for families dealing with mental health challenges. The [Name of a National Mental Health Organization, e.g., National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI)] provides information, support groups, and advocacy for individuals and families affected by mental illness. Their website and helpline offer valuable resources, including finding local support groups and connecting with mental health professionals.
Similarly, the [Name of a Child Mental Health Organization, e.g., Child Mind Institute] focuses on children’s mental health and offers resources for parents and caregivers. They provide educational materials, expert advice, and resources to help families navigate the challenges of mental health issues in children. Contact information for these and other relevant organizations can be readily found through online searches.
Remember to utilize your health insurance provider’s directory to locate mental health professionals in your network.
Mindfulness Practices for Children and Parents
Mindfulness, the practice of paying attention to the present moment without judgment, offers significant benefits for both children and parents navigating the stresses of daily life. By cultivating awareness of thoughts, feelings, and sensations, individuals can develop greater emotional regulation, improved focus, and increased resilience. Introducing mindfulness practices into family routines can foster a calmer, more connected environment.Mindfulness exercises can be adapted to suit different age groups and developmental stages, making them accessible to children of all ages.
The key is to present the practices in a playful, engaging manner, making them fun and enjoyable rather than a chore.
Mindfulness Exercises for Different Age Groups
Mindfulness practices for children should be age-appropriate and engaging. Younger children benefit from shorter, more playful activities, while older children can engage in more complex techniques.
- Preschool (Ages 3-5): Simple breathing exercises, like blowing bubbles or pretending to smell flowers, can introduce the concept of focusing on the present. Listening to calming music and engaging in sensory activities, such as playing with playdough or sand, can also promote mindfulness. A focus on noticing colors, shapes, and textures during playtime can encourage present moment awareness.
- Elementary School (Ages 6-12): Guided meditations focusing on body scans or visualizations are effective. Mindful movement activities, such as yoga or tai chi, can help children connect their minds and bodies. Nature walks, paying attention to sounds and sights, can also be a great mindfulness exercise. Mindful eating, paying attention to the taste, texture, and smell of food, is another valuable practice.
- Teenagers (Ages 13-18): Teenagers can benefit from more sophisticated mindfulness techniques, such as mindful listening, journaling, or using mindfulness apps. Engaging in activities like mindful drawing or creative writing can promote self-expression and self-awareness. They can also explore more advanced meditation techniques, focusing on longer periods of stillness and observation.
Benefits of Mindfulness for Stress and Anxiety Reduction
Mindfulness cultivates a sense of calm and reduces the intensity of stressful situations. By focusing on the present moment, children and parents learn to observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment, preventing them from becoming overwhelmed by anxiety. Regular mindfulness practice strengthens the ability to manage emotional responses, reducing reactivity and promoting a sense of control. Studies have shown a correlation between mindfulness practice and decreased levels of cortisol, the stress hormone.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology demonstrated that mindfulness-based interventions significantly reduced anxiety symptoms in adolescents.
Mindfulness and Improved Focus and Emotional Regulation
Mindfulness enhances attention span and focus by training the mind to resist distractions and stay present. This improved focus translates to better academic performance, improved concentration during tasks, and increased productivity. Furthermore, mindfulness fosters emotional regulation by helping individuals identify and understand their emotions without judgment. This self-awareness empowers them to respond to challenging situations more effectively, reducing impulsive reactions and promoting healthy coping mechanisms.
For instance, a child learning to recognize the physical sensations of anger (e.g., clenched fists, rapid heartbeat) through mindfulness can then learn to employ calming techniques before reacting angrily.
Step-by-Step Guide to a Simple Mindfulness Meditation for Children
This meditation is suitable for children aged 6 and above. It emphasizes gentle guidance and encourages a playful approach to the practice.
- Find a comfortable position: Sit or lie down in a quiet space. Encourage children to find a position where they feel relaxed and comfortable.
- Close your eyes gently: If closing their eyes is uncomfortable, they can keep them softly focused on a single point.
- Focus on your breath: Guide the child to notice the sensation of their breath entering and leaving their body. They can pay attention to the rise and fall of their belly or chest.
- Notice your thoughts and feelings: Encourage the child to observe any thoughts or feelings that arise without judgment. Explain that thoughts are like clouds passing by; they don’t have to be chased or held onto.
- Bring your attention back to your breath: When the child’s mind wanders, gently guide their attention back to the sensation of their breath. This is a natural part of the process.
- Continue for 5-10 minutes: Start with shorter sessions and gradually increase the duration as the child becomes more comfortable.
- Open your eyes gently: When ready, gently open their eyes and take a moment to notice how they feel.
Mental Health Advocacy and Resources
Children with allergies often face significant mental health challenges, ranging from anxiety and depression related to managing their condition to social isolation stemming from dietary restrictions or fear of allergic reactions. Effective advocacy is crucial to ensure these children receive the support they need to thrive. This section explores the importance of mental health advocacy and provides resources to help families navigate these complexities.Advocating for children’s mental health needs is essential for their well-being and overall development.
It involves actively working to create a supportive environment where their unique needs are understood and addressed. Early intervention is particularly critical, as it can significantly improve outcomes and prevent the escalation of mental health challenges.
The Importance of Mental Health Advocacy for Children with Allergies
Children with allergies often experience heightened anxiety surrounding potential allergic reactions, impacting their daily routines, social interactions, and overall quality of life. This anxiety can manifest in various ways, from avoidance behaviors to panic attacks. Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in advocating for their children’s mental health needs, ensuring they receive appropriate support and accommodations in school and community settings.
This advocacy can involve educating teachers and peers about allergies, securing necessary medical accommodations, and seeking professional mental health support when needed. The goal is to create an environment where the child feels safe, understood, and empowered to manage their condition.
Advocating for Children’s Mental Health Needs in Schools and Communities
Effective advocacy requires a multifaceted approach. In schools, this may involve working with school administrators, teachers, and nurses to develop allergy management plans, educate staff on allergy symptoms and emergency procedures, and implement strategies to minimize the risk of allergic reactions. This could include establishing designated allergy-safe zones, providing training on the use of epinephrine auto-injectors, and ensuring access to necessary medications.
In the community, advocacy can involve raising awareness about allergies and mental health through community events, workshops, and partnerships with local organizations. Collaborating with healthcare providers, mental health professionals, and support groups can also provide valuable resources and guidance. A proactive and informed approach ensures that children with allergies receive the necessary support to manage their condition and thrive in all aspects of their lives.
Benefits of Early Intervention for Mental Health Challenges
Early intervention for mental health challenges in children with allergies is vital for several reasons. Early identification and treatment can prevent the escalation of problems, leading to improved long-term outcomes. Early intervention can minimize the impact of mental health issues on academic performance, social relationships, and overall well-being. Moreover, early intervention can help children develop coping mechanisms and strategies to manage their allergies and related anxieties more effectively.
For example, a child who receives early intervention for anxiety related to food allergies may learn relaxation techniques and develop a sense of control over their situation, leading to improved self-esteem and reduced anxiety. Early intervention can also help prevent the development of more severe mental health conditions later in life.
Mental Health Resources
The following table provides examples of resource types and contact information. Remember to verify contact information independently, as it may change.
| Resource Type | Contact Information |
|---|---|
| National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) | Find your local chapter through their website or by searching online for “NAMI [your state/city]”. |
| Child Mind Institute | Search online for “Child Mind Institute” to find their contact information and resources. |
| The Jed Foundation | Search online for “The Jed Foundation” to find their contact information and resources. |
| Local Mental Health Clinics | Contact your primary care physician or health insurance provider for referrals to local mental health clinics. |
| School Counselor or Psychologist | Contact your child’s school to connect with their counselor or psychologist. |
Therapy and Counseling Options
Living with allergies, especially for children, can significantly impact mental well-being. The constant worry about reactions, the limitations imposed, and the need for careful planning can lead to stress and anxiety for both children and their families. Therapy and counseling offer valuable support in navigating these challenges. Different approaches can address specific needs, promoting emotional resilience and improved coping mechanisms.
Types of Therapy Beneficial for Children with Allergies and Their Families
Several therapeutic approaches can be highly beneficial for children with allergies and their families. These methods help address the emotional and psychological impact of living with allergies, fostering better management and improved quality of life. Individual therapy, for instance, provides a safe space for children to express their feelings about their allergies and learn coping strategies. Family therapy helps improve communication and collaboration between family members, crucial in managing the complexities of allergy management.
Play therapy, particularly useful for younger children, allows them to express their anxieties and concerns through play, making the therapeutic process more accessible and engaging.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Anxiety Management
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a highly effective approach for managing anxiety related to allergies. CBT helps children identify and challenge negative thought patterns and beliefs associated with their allergies. For example, a child might fear a severe allergic reaction at school. CBT would help them examine the likelihood of this happening, develop coping strategies for managing their anxiety (like deep breathing exercises), and challenge catastrophic thinking.
By changing negative thought patterns and developing practical coping mechanisms, CBT empowers children to feel more in control and less anxious about their allergies. The therapist would work with the child to create personalized strategies tailored to their specific anxieties and challenges.
Benefits of Family Therapy in Addressing Allergy-Related Stress
Family therapy plays a crucial role in managing the stress associated with childhood allergies. It provides a platform for open communication and collaboration among family members, ensuring everyone understands the challenges and responsibilities involved in allergy management. Family therapy helps families develop strategies for managing allergy-related disruptions to daily life, such as meal planning, social events, and travel. The therapist helps family members improve their communication skills, reduce conflict, and build stronger support systems.
This collaborative approach can significantly reduce the overall stress and burden on the family, improving everyone’s emotional well-being. For instance, a family might struggle with disagreements about how strictly to follow allergy protocols. Family therapy can help them find a balance that works for everyone while prioritizing the child’s safety.
Examples of Therapy Helping Children Develop Coping Skills
Therapy can equip children with a range of coping skills to manage their allergies and associated anxieties. For example, a child might learn relaxation techniques like deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation to calm themselves during an anxiety-provoking situation. They might also learn problem-solving skills to anticipate and manage potential allergy triggers. Role-playing scenarios, such as interacting with friends who might offer them food containing allergens, can help children practice assertive communication and self-advocacy.
Furthermore, therapists can help children develop self-soothing strategies, such as using a comfort object or engaging in a calming activity, to manage anxiety in challenging situations. These coping mechanisms empower children to feel more confident and in control of their lives, despite living with allergies.
Building Resilience in Children with Allergies
Living with allergies can present significant challenges for children, impacting their daily lives, social interactions, and overall well-being. Building resilience – the ability to bounce back from adversity – is crucial for children navigating these difficulties. This involves fostering a positive self-image, equipping them with coping mechanisms, and strengthening their support networks.
Resilience isn’t about avoiding hardship; it’s about developing the skills and mindset to navigate it successfully. For children with allergies, this means learning to manage their condition effectively, cope with unexpected reactions, and maintain a positive outlook despite limitations. This process empowers them to not only endure challenges but also to learn and grow from them, fostering a sense of control and self-confidence.
Positive Self-Esteem and Self-Efficacy
Positive self-esteem and self-efficacy are cornerstones of resilience. Children with high self-esteem believe in their abilities and worth, even when facing setbacks. Self-efficacy, the belief in one’s capacity to succeed in specific situations, is particularly important for managing allergies. When a child believes they can effectively manage their allergy symptoms and avoid triggers, they are more likely to cope with stressful situations and maintain a positive outlook.
This confidence can be nurtured through consistent positive reinforcement, celebrating successes (no matter how small), and focusing on their strengths. For example, praising a child for diligently following their allergy management plan, even when it’s inconvenient, reinforces their self-efficacy and builds their confidence in their ability to handle their condition.
The Role of Social Support in Building Resilience
Strong social support networks are vital for building resilience in children with allergies. Feeling understood, accepted, and supported by family, friends, and peers can significantly buffer the negative impacts of their condition. Open communication within the family about allergies, including potential anxieties and challenges, is crucial. Schools can also play a vital role by providing a supportive and inclusive environment, educating peers about allergies, and ensuring appropriate accommodations are in place.
Connecting children with other children who have allergies can foster a sense of belonging and shared understanding, reducing feelings of isolation and promoting peer support. A child might find comfort and advice from another child who also carries an EpiPen, for instance.
Activities that Promote Resilience in Children
Developing resilience is an ongoing process that requires consistent effort. Here are some activities that can promote resilience in children with allergies:
Engaging in these activities helps children develop coping mechanisms, problem-solving skills, and a sense of control over their lives, which are all essential components of resilience.
- Problem-solving activities: Role-playing scenarios involving allergy triggers and reactions helps children develop strategies for managing difficult situations. For example, role-playing a scenario where a friend accidentally gives them a food containing a known allergen helps them practice assertive communication and self-advocacy skills.
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, can help children manage stress and anxiety related to their allergies. These techniques can help them regulate their emotions and respond to challenging situations more effectively.
- Physical activity and healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise and a healthy diet contribute to overall well-being and can improve a child’s ability to cope with stress. A healthy lifestyle helps build physical resilience, making them better equipped to handle allergy-related challenges.
- Creative expression: Engaging in creative activities, such as art, music, or writing, can provide a healthy outlet for expressing emotions and building self-esteem. Children can express their feelings and experiences related to their allergies through creative means.
- Building positive relationships: Encouraging participation in social activities and fostering positive relationships with peers and adults strengthens social support networks and builds a sense of belonging. This can mitigate feelings of isolation and increase their ability to cope with adversity.
Sleep and Mental Health in Relation to Allergies: Allergies In Children
Allergies significantly impact a child’s sleep, creating a ripple effect that can negatively influence their mental well-being. Disrupted sleep due to allergic reactions can lead to daytime fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating, all of which can exacerbate existing mental health challenges or contribute to the development of new ones. Understanding this connection is crucial for parents and caregivers in supporting their children’s overall health.Allergic reactions, whether it’s nasal congestion from hay fever, coughing fits from asthma, or skin irritation from eczema, can disrupt sleep patterns in children.
The discomfort and physical symptoms associated with allergies often lead to frequent awakenings throughout the night, resulting in poor sleep quality and insufficient restorative rest. This lack of sleep can then contribute to increased anxiety, irritability, difficulty focusing in school, and even depressive symptoms. The constant cycle of poor sleep and worsened allergy symptoms can create a vicious cycle, negatively impacting both physical and mental health.
Impact of Allergies on Sleep Quality in Children
Allergies frequently manifest as nighttime symptoms. Nasal congestion makes breathing difficult, leading to restless sleep and frequent awakenings. Similarly, allergic asthma can trigger coughing and wheezing, disrupting sleep and causing anxiety about the next attack. Itchy skin from eczema can also prevent a child from getting a restful night’s sleep. The cumulative effect of these disruptions significantly reduces the amount of quality sleep a child receives, impacting their daytime functioning and overall well-being.
For example, a child with severe seasonal allergies might experience several hours of fragmented sleep each night, leaving them exhausted and irritable during the day.
Connection Between Sleep Disturbances and Mental Health Challenges
Insufficient sleep directly impacts a child’s emotional regulation and cognitive function. Sleep deprivation can lead to increased irritability, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating, all of which can worsen existing anxiety or depression. Furthermore, chronic sleep disturbances can increase the risk of developing mental health problems in children. Studies have shown a strong correlation between poor sleep quality and an increased likelihood of anxiety disorders, depression, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
For instance, a child already predisposed to anxiety might experience significantly heightened anxiety levels due to sleep deprivation caused by allergic reactions.
Strategies for Improving Sleep Hygiene in Children with Allergies
Establishing good sleep hygiene is essential for children with allergies. This involves creating a consistent sleep schedule, ensuring a comfortable and allergen-free sleep environment, and implementing strategies to manage allergy symptoms at night. This might include using air purifiers with HEPA filters to remove allergens from the bedroom, regularly washing bedding in hot water, and using hypoallergenic pillows and mattress covers.
Medical interventions such as allergy medication, taken as prescribed by a physician, can also significantly improve sleep quality. Regular exercise during the day can also promote better sleep, as long as it is not performed too close to bedtime.
Creating a Relaxing Bedtime Routine for Children
A consistent and calming bedtime routine can significantly improve sleep quality. This could involve a warm bath, reading a book together, or quiet playtime. Creating a relaxing atmosphere in the bedroom is also crucial. This might include dimming the lights, using calming scents like lavender, and playing soft, soothing music. Avoiding screen time before bed is also important, as the blue light emitted from electronic devices can interfere with melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep.
A consistent bedtime and wake-up time, even on weekends, can help regulate the child’s internal clock and promote better sleep. The routine should be adaptable to the child’s age and preferences, but consistency is key.
Workplace Mental Health for Parents of Allergic Children
Parenting a child with allergies presents unique challenges, and these challenges often extend into the workplace. The constant worry about accidental exposures, managing medication schedules, and navigating school and healthcare systems can significantly impact a parent’s mental well-being and job performance. The emotional toll can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and even burnout, affecting both professional and personal life.The importance of workplace support for parents of allergic children cannot be overstated.
A supportive work environment can be the difference between managing stress effectively and experiencing a significant decline in mental health. Understanding and accommodation from employers can alleviate some of the pressures, allowing parents to focus on both their work and their child’s needs. This, in turn, leads to improved productivity, reduced absenteeism, and a more engaged workforce.
Challenges Faced by Parents in the Workplace
Parents of allergic children often face difficulties balancing work and the demanding needs of their child’s allergy management. These include scheduling flexibility for doctor’s appointments, school interactions, and emergency situations. The constant worry about potential allergic reactions can lead to distractions at work and decreased concentration. Furthermore, the need to educate colleagues, manage workplace environments to minimize allergen exposure, and advocate for their child’s needs can add significant pressure to an already demanding work schedule.
This can manifest as increased stress, anxiety, and difficulty focusing on work tasks. The lack of understanding or support from colleagues or supervisors can further exacerbate these challenges. For example, a parent might struggle to take time off for unexpected allergy-related emergencies without facing negative repercussions at work.
Strategies for Managing Work-Life Balance
Effective strategies for managing work-life balance are crucial for parents of allergic children. Open communication with supervisors about the child’s allergies and the potential need for flexibility is essential. This might involve discussing flexible work arrangements, such as working from home occasionally or adjusting work hours. Prioritizing tasks and utilizing time management techniques can help reduce stress and improve efficiency.
Seeking support from employee assistance programs (EAPs) or mental health professionals can provide valuable coping mechanisms and stress-reduction strategies. Building a strong support network, whether through family, friends, or support groups, can also significantly improve a parent’s ability to navigate the challenges of raising a child with allergies.
Resources Available to Support Parents in the Workplace
It is vital for parents to understand the resources available to them. Access to these resources can significantly alleviate the burden of managing a child’s allergies while maintaining a successful career.
- Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): Many companies offer EAPs that provide confidential counseling, stress management resources, and referrals to mental health professionals.
- Flexible Work Arrangements: Discussing options like telecommuting, compressed workweeks, or flexible hours with employers can significantly improve work-life balance.
- Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA): This federal law provides eligible employees with unpaid, job-protected leave for serious medical conditions, including those affecting their children.
- Support Groups and Online Communities: Connecting with other parents facing similar challenges can offer valuable emotional support and practical advice.
- Human Resources Department: HR departments can often provide information on company policies related to leave, flexible work arrangements, and employee assistance programs.
Overcoming Addictions Related to Stress Management
Living with a child who has allergies can be incredibly stressful. The constant worry about accidental exposures, managing medications, and navigating social situations can take a significant toll on parents and caregivers. Unfortunately, this stress can sometimes lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms, including substance abuse. Understanding this link is crucial for supporting families affected by childhood allergies.The pressure of managing a child’s allergies can feel overwhelming, leading some parents to turn to alcohol, drugs, or other addictive behaviors as a means of escape.
This is not a sign of weakness, but rather a reflection of the immense burden these families carry. These unhealthy coping mechanisms offer temporary relief but ultimately exacerbate the underlying issues, creating a cycle of stress and addiction. The long-term consequences can be devastating, impacting not only the parent’s physical and mental health but also the well-being of the entire family.
Seeking Help for Addiction
Recognizing the need for help is the first critical step in overcoming addiction. Addiction is a treatable condition, and there are many effective resources available to support individuals and families. Delaying treatment can lead to more severe consequences, so seeking professional help as soon as possible is vital. Support groups, therapy, and medication-assisted treatment can all play an important role in recovery.
Addiction Treatment and Recovery Resources
Several resources offer comprehensive support for addiction treatment and recovery. These include:
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA): SAMHSA’s National Helpline provides confidential treatment referral and information services, connecting individuals with local treatment facilities and support groups. They offer a wide range of resources and can help individuals find appropriate care based on their specific needs and insurance coverage.
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA): NIDA provides extensive information about drug abuse and addiction, including treatment options and research findings. Their website offers valuable resources for understanding addiction and navigating the recovery process.
- Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and Narcotics Anonymous (NA): These 12-step programs offer peer support and guidance to individuals struggling with alcohol and drug addiction. These groups provide a safe and supportive environment for sharing experiences and working towards recovery.
- Local Treatment Centers and Hospitals: Many hospitals and specialized treatment centers offer comprehensive addiction treatment programs, including detoxification, therapy, and ongoing support.
Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Replacing unhealthy coping mechanisms with healthy alternatives is essential for long-term well-being. These strategies can help manage stress and promote emotional regulation:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. Even a short walk can make a difference.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: These practices can help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and feelings, allowing them to manage stress more effectively.
- Connecting with Support Systems: Talking to friends, family, or support groups can provide emotional support and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Engaging in Hobbies: Spending time on enjoyable activities can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Seeking Professional Help: Therapists and counselors can provide guidance and support in developing healthy coping mechanisms and addressing underlying issues contributing to stress and addiction.
Personal Growth and Self-Care for Parents

Parenting a child with allergies can be incredibly demanding, both emotionally and physically. The constant vigilance, worry, and potential for emergencies can leave parents feeling depleted and overwhelmed. Prioritizing personal growth and self-care is not selfish; it’s essential for maintaining mental and physical well-being and ultimately, for being the best parent you can be. Investing in your own well-being allows you to better manage the challenges of raising a child with allergies and strengthens your ability to support your family effectively.The importance of setting boundaries and prioritizing self-care cannot be overstated.
Parents often struggle to separate their roles as caregivers from their individual identities. However, neglecting your own needs ultimately diminishes your capacity to care for others. Setting healthy boundaries, such as limiting screen time, delegating tasks, or saying no to additional commitments, allows you to reclaim time and energy for yourself. This conscious effort to prioritize self-care isn’t about indulgence; it’s about sustainable well-being, ensuring you can continue providing care for your child effectively.
Benefits of Engaging in Hobbies and Activities Outside of Parenting
Engaging in hobbies and activities unrelated to parenting offers a crucial mental and emotional respite. These activities provide opportunities for relaxation, stress reduction, and the rediscovery of personal interests. Participating in hobbies allows parents to reconnect with themselves outside of their parental role, fostering a sense of identity beyond caregiving. This renewed sense of self can lead to increased patience, improved emotional regulation, and a more balanced approach to parenting.
For example, a parent who enjoys painting might find that an hour spent painting helps them de-stress and return to their family feeling refreshed and capable. Similarly, regular exercise can release endorphins and improve overall mood, leading to increased resilience in the face of allergy-related challenges.
Self-Care Activities for Parents
It’s crucial to actively incorporate self-care into your daily routine. Even small acts of self-care can accumulate significant positive effects on your overall well-being. Remember that self-care is not a luxury but a necessity for parents navigating the complexities of raising a child with allergies.
- Regular exercise: Even a short walk can significantly improve mood and energy levels.
- Mindfulness and meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
- Spending time in nature: Connecting with nature has been shown to reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
- Engaging in hobbies: Dedicate time to activities you enjoy, such as reading, painting, or playing a musical instrument.
- Connecting with friends and family: Maintaining social connections provides emotional support and reduces feelings of isolation.
- Prioritizing sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for both physical and mental health.
- Seeking professional support: Don’t hesitate to reach out to a therapist or counselor if you’re struggling to cope.
- Setting boundaries: Learn to say no to commitments that overwhelm you.
- Practicing gratitude: Focusing on positive aspects of your life can improve overall mood and outlook.
- Taking breaks throughout the day: Short breaks can help prevent burnout and improve focus.
Navigating the complexities of childhood allergies requires a multifaceted approach encompassing medical expertise, family support, and proactive mental health strategies. This guide has highlighted the crucial interplay between physical health and emotional well-being in children with allergies. By understanding the various types of allergies, employing effective management techniques, and addressing the associated stress and anxiety, parents and caregivers can empower their children to thrive despite their allergies, leading to improved quality of life for the entire family.
Helpful Answers
What are the most common food allergies in children?
Milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish are among the most prevalent food allergens in children.
How long do food allergies typically last?
The duration varies; some allergies may resolve over time (e.g., milk allergy), while others can persist into adulthood (e.g., peanut allergy).
My child has a mild allergy; do they still need to see a doctor?
Even mild allergies require medical evaluation for proper diagnosis and management to prevent escalation of symptoms.
What is anaphylaxis and how is it treated?
Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction requiring immediate emergency medical attention, often involving an epinephrine injection (EpiPen).
Can allergies develop later in childhood?
Yes, new allergies can develop at any age, although many appear during early childhood.



