Preventing Diabetic Complications A Comprehensive Guide

Preventing diabetic complications is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Diabetes, if left unmanaged, can lead to a cascade of serious health issues affecting the eyes, kidneys, heart, and feet. This comprehensive guide explores various strategies and approaches to effectively manage diabetes and mitigate the risk of developing these complications. We will delve into practical steps for managing blood sugar levels, maintaining healthy lifestyles, and seeking appropriate medical care to minimize long-term health risks.
From understanding the importance of regular foot examinations and proper hygiene to mastering blood sugar control through diet, exercise, and medication, this guide provides a roadmap to navigating the complexities of diabetes management. We will also address the mental health aspects often associated with living with diabetes, offering practical advice on stress management, coping mechanisms, and seeking support when needed.
The ultimate goal is to empower individuals with diabetes to proactively manage their condition and live fulfilling, healthy lives.
Blood Sugar Control

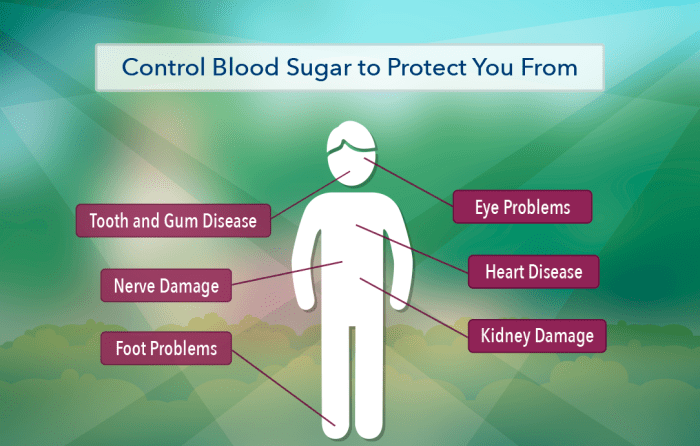
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing and managing diabetic complications. This involves a multifaceted approach encompassing dietary choices, regular physical activity, and, in many cases, medication management. Effective blood sugar control significantly reduces the risk of long-term health problems associated with diabetes.
Dietary Strategies for Blood Sugar Management
A well-planned diet plays a pivotal role in regulating blood sugar. Focusing on foods with a low glycemic index (GI) helps prevent rapid spikes in blood glucose. This means choosing complex carbohydrates over simple sugars, and incorporating lean proteins and healthy fats into each meal. Portion control is also essential to avoid overconsumption of carbohydrates.
Sample Meal Plan
A sample meal plan might include:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and a sprinkle of nuts.
- Lunch: Salad with grilled chicken or fish, and a whole-wheat roll.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted vegetables and brown rice.
- Snacks: A handful of almonds, a piece of fruit, or a small serving of Greek yogurt.
This is just a sample, and individual needs may vary. Consulting a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator can help create a personalized meal plan tailored to specific dietary needs and preferences.
The Importance of Regular Exercise in Blood Glucose Control
Regular physical activity is another cornerstone of effective blood sugar management. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, meaning your body uses insulin more effectively to transport glucose from the bloodstream into cells. This leads to lower blood sugar levels.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Exercise enhances the body’s ability to utilize insulin, leading to better glucose uptake by cells.
- Weight Management: Physical activity contributes to weight loss or maintenance, which is beneficial for blood sugar control.
- Reduced Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Exercise helps manage cardiovascular risk factors often associated with diabetes.
- Increased Energy Levels: Regular physical activity boosts overall energy levels and improves mood.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread throughout the week. Incorporate strength training exercises at least two days per week.
Insulin and Oral Medications for Diabetes
Many individuals with diabetes require medication to manage their blood sugar levels. Insulin therapy is often necessary for people with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes. Insulin mimics the action of the body’s natural insulin, helping glucose enter cells. Oral medications work in various ways, such as stimulating insulin production, improving insulin sensitivity, or slowing down glucose absorption from the digestive tract.
The type and dosage of medication are determined by a healthcare professional based on individual needs and response. Careful adherence to the prescribed medication regimen is crucial.
Effective Blood Sugar Monitoring and Interpretation
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management. This involves using a blood glucose meter to measure blood sugar levels at various times throughout the day. Understanding how different factors influence blood sugar levels, such as meals, exercise, and medication, helps individuals make informed decisions about their diabetes management. Keeping a log of blood sugar readings and sharing them with a healthcare professional is vital for adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Consistent monitoring allows for early detection of potential problems and helps optimize blood sugar control. For example, consistently high readings might necessitate adjustments to medication or diet, while consistently low readings might require changes to meal timing or medication.
Eye Care for Diabetics
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of developing various eye diseases, primarily due to its impact on blood vessels. High blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, leading to a range of complications. Understanding the connection between diabetes and eye health is crucial for preventing vision loss.Diabetic retinopathy is the most common diabetic eye disease, resulting from damage to the retina’s blood vessels.
This damage can cause blurry vision, floaters, and eventually blindness if left untreated. Another serious complication is diabetic macular edema (DME), a swelling of the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. This can lead to significant vision impairment. Glaucoma, characterized by increased pressure within the eye, also occurs more frequently in people with diabetes.
The damage to blood vessels can also increase the risk of cataracts, clouding of the eye’s lens.
The Importance of Regular Dilated Eye Exams
Regular dilated eye exams are essential for early detection of diabetic retinopathy and other eye diseases. During a dilated eye exam, eye drops are used to widen the pupils, allowing the ophthalmologist to get a clear view of the retina. This detailed examination enables the early detection of even subtle changes in the blood vessels, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
The American Diabetes Association recommends annual dilated eye exams for people with diabetes, even if they have no symptoms. Early detection significantly improves the chances of preventing or delaying vision loss. For individuals with existing retinopathy, more frequent monitoring might be necessary.
Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
Treatment options for diabetic retinopathy vary depending on the severity of the disease. For mild cases, regular monitoring and strict blood sugar control may be sufficient to prevent progression. For more advanced cases, various treatments are available. Laser photocoagulation is a common procedure that uses a laser to seal off leaking or damaged blood vessels, reducing swelling and preventing further damage.
Anti-VEGF injections are another effective treatment, involving injections into the eye that block the growth of abnormal blood vessels. In some severe cases, vitrectomy surgery may be necessary to remove scar tissue or blood from the vitreous gel, the clear gel that fills the eye. The specific treatment plan is determined by the ophthalmologist based on the individual’s condition and the severity of the retinopathy.
Maintaining Good Eye Health to Reduce Vision Loss Risk
Maintaining good overall health is paramount in preventing diabetic eye complications. This includes diligently managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication as prescribed by a physician. Regular blood pressure and cholesterol monitoring are also vital, as these factors contribute to vascular health. Quitting smoking is crucial, as smoking accelerates the progression of diabetic retinopathy. A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can support overall eye health.
Protecting eyes from sunlight through the use of sunglasses with UV protection is also important. Finally, regular comprehensive eye examinations are indispensable for early detection and timely intervention. Following these guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of vision loss associated with diabetes.
Kidney Health and Diabetes
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of developing kidney disease, a condition known as diabetic nephropathy. This occurs because high blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste products from the blood. Over time, this damage can lead to kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Diabetic Nephropathy: The Link Between Diabetes and Kidney Damage
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels cause damage to the glomeruli, the filtering units of the kidneys. This damage leads to the leakage of protein into the urine (albuminuria), a key indicator of kidney disease. As the damage progresses, the kidneys lose their ability to effectively filter waste and excess fluid, resulting in a build-up of toxins in the body and potentially leading to kidney failure.
The severity of diabetic nephropathy is directly related to the duration and control of blood sugar levels. Poorly controlled blood sugar significantly accelerates the progression of kidney damage.
Early Warning Signs of Diabetic Kidney Damage
Early detection is crucial in managing diabetic nephropathy. While early stages often show no symptoms, regular check-ups are vital. Key indicators include the presence of albumin in the urine (microalbuminuria), which can be detected through a simple urine test. Elevated blood pressure is another significant warning sign, often preceding noticeable kidney damage. Persistent swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet, and unexplained fatigue or shortness of breath can also indicate advanced kidney damage.
Regular blood tests to assess kidney function (e.g., eGFR – estimated glomerular filtration rate) are essential for early diagnosis and monitoring.
Blood Pressure Management and Kidney Protection
Maintaining healthy blood pressure is paramount in preventing and slowing the progression of diabetic nephropathy. High blood pressure puts extra strain on the already damaged kidneys, accelerating the deterioration process. Effective blood pressure management involves lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise, and in many cases, medication. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are commonly prescribed medications that help lower blood pressure and protect the kidneys by reducing protein leakage.
Careful monitoring of blood pressure is essential, with regular check-ups and adjustments to medication as needed.
Lifestyle Modifications to Prevent or Slow Diabetic Nephropathy
Lifestyle changes play a vital role in preventing or slowing the progression of diabetic nephropathy. These changes center around strict blood sugar control, achieved through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adherence to any prescribed medication. Maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial, as obesity exacerbates many diabetic complications, including kidney disease. A diet low in sodium, saturated fats, and cholesterol is recommended to help manage blood pressure.
Regular physical activity improves overall health and helps control blood sugar and blood pressure. Quitting smoking, if applicable, is also essential, as smoking further damages blood vessels. Finally, staying well-hydrated helps the kidneys function optimally. Consistent adherence to these lifestyle changes significantly improves the chances of preventing or slowing the progression of diabetic nephropathy.
Heart Health and Diabetes
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), encompassing conditions like coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. This heightened risk stems from several interconnected factors, including damage to blood vessels caused by high blood sugar levels, increased inflammation, and abnormal lipid profiles. Understanding and actively managing these risks is crucial for individuals with diabetes to improve their overall health and longevity.
Increased Cardiovascular Disease Risk in People with Diabetes
High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels over time, making them more prone to hardening and narrowing (atherosclerosis). This process restricts blood flow, leading to reduced oxygen supply to the heart and other organs. Furthermore, diabetes often contributes to elevated blood pressure and cholesterol levels, exacerbating the risk of CVD. Diabetic individuals are also more susceptible to blood clot formation, increasing the likelihood of heart attacks and strokes.
The longer someone has diabetes, and the poorer their blood sugar control, the greater their risk becomes. For instance, a person with poorly managed type 1 diabetes for 20 years has a substantially higher risk of developing heart disease compared to a healthy individual of the same age.
Cholesterol and Blood Pressure Management in Diabetics, Preventing diabetic complications
Maintaining healthy cholesterol and blood pressure levels is paramount for preventing cardiovascular complications in people with diabetes. High cholesterol, particularly LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, contributes to plaque buildup in arteries. Similarly, persistently high blood pressure puts extra strain on the heart and blood vessels, accelerating the damage caused by diabetes. Regular monitoring of cholesterol and blood pressure, along with lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, medication, are essential components of cardiovascular risk reduction.
For example, a diabetic individual might need to follow a low-saturated fat diet and take statins to lower their LDL cholesterol levels. Similarly, they might require antihypertensive medications to control their blood pressure.
Role of Diet and Exercise in Reducing Cardiovascular Risks
A heart-healthy diet plays a vital role in managing diabetes and reducing cardiovascular risk. This involves consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, while limiting saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium. Regular physical activity is equally important. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, improve blood pressure, and contribute to weight management—all of which positively impact cardiovascular health.
Aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training twice a week, is generally recommended. For example, brisk walking, swimming, or cycling are excellent forms of aerobic exercise, while weightlifting or bodyweight exercises are beneficial for strength training.
Medications for Cardiovascular Health in Diabetics
Several medications are available to help manage cardiovascular risk in people with diabetes. Statins are commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol levels. Antihypertensive medications, such as ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers, help control blood pressure. Aspirin may be recommended to reduce the risk of blood clots. In some cases, medications to improve blood sugar control, such as metformin or insulin, may also indirectly benefit cardiovascular health by better managing blood glucose levels.
The choice of medication depends on individual needs and risk factors, determined by a healthcare professional. For instance, a patient with both high cholesterol and high blood pressure might be prescribed both a statin and an ACE inhibitor.
Stress and Anxiety Management
Living with diabetes can be challenging, and the constant monitoring, medication management, and potential complications can significantly contribute to stress and anxiety. Effectively managing these emotional responses is crucial for overall well-being and successful diabetes management. Untreated stress can even negatively impact blood sugar control, creating a vicious cycle. This section Artikels strategies to develop a personalized stress management plan and cope with anxiety related to diabetes.
Designing a Stress Management Plan Incorporating Relaxation Techniques
A proactive approach to stress management involves incorporating regular relaxation techniques into your daily routine. These techniques help to calm the nervous system and reduce the physiological effects of stress. For example, deep breathing exercises, where you focus on slow, deep inhalations and exhalations, can quickly lower heart rate and blood pressure. Progressive muscle relaxation involves systematically tensing and releasing different muscle groups to relieve muscle tension often associated with stress.
Guided imagery, where you visualize peaceful scenes, can also promote relaxation and reduce anxiety. Finding the techniques that work best for you may require experimentation, but consistency is key. Consider scheduling these practices into your daily calendar, just like any other important appointment.
Practical Strategies for Coping with Anxiety Related to Diabetes Management
Anxiety related to diabetes can manifest in various ways, from fear of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) to worry about long-term complications. Practical strategies can help mitigate these anxieties. Keeping a detailed log of your blood sugar levels, meals, and medications can provide a sense of control and predictability. Open communication with your healthcare team is essential; discussing your concerns and anxieties can lead to tailored management plans and address any misunderstandings.
Joining a support group connects you with others facing similar challenges, fostering a sense of community and shared understanding. Learning about diabetes in detail can also reduce anxiety by empowering you with knowledge and reducing uncertainty.
Mindfulness Practices to Improve Emotional Well-being
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and yoga, focus on being present in the moment without judgment. Regular mindfulness practice can significantly improve emotional well-being by reducing stress and anxiety. Mindfulness meditation involves focusing on your breath, body sensations, or sounds without getting carried away by thoughts or emotions. Yoga combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation, promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
Even short, daily mindfulness sessions can make a noticeable difference in managing stress and anxiety associated with diabetes. The consistent practice cultivates a sense of calm and emotional resilience.
Resources for Stress Reduction and Anxiety Management
Numerous resources are available to support stress reduction and anxiety management. These include online resources offering guided meditations, relaxation techniques, and information on diabetes management. Many apps provide mindfulness exercises and tools for tracking stress levels. Local support groups offer a sense of community and peer support. Therapists specializing in stress management and anxiety disorders can provide individual support and develop personalized coping strategies.
Your healthcare provider can also recommend resources and support tailored to your individual needs. Utilizing these resources can provide valuable support and enhance your overall well-being while managing diabetes.
Depression Support Resources
Living with diabetes can be challenging, and it’s not uncommon for individuals to experience depression. The emotional toll of managing the condition, along with potential physical complications, can significantly impact mental well-being. Understanding the signs of depression and accessing appropriate support is crucial for improving overall health and quality of life for people with diabetes.The connection between diabetes and depression is complex and bidirectional.
Diabetes can increase the risk of depression, and conversely, depression can make managing diabetes more difficult. Untreated depression can lead to poorer blood sugar control, reduced adherence to treatment plans, and an increased risk of complications. Therefore, addressing depression is an essential aspect of comprehensive diabetes care.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Depression in Individuals with Diabetes
Recognizing the symptoms of depression is the first step towards seeking help. While the experience of depression varies from person to person, some common signs in individuals with diabetes include persistent sadness or low mood, loss of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed, fatigue or low energy, feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt, difficulty concentrating or making decisions, changes in appetite or weight, sleep disturbances (insomnia or excessive sleeping), and thoughts of death or suicide.
It’s important to note that experiencing some of these symptoms occasionally is normal, but persistent symptoms warrant professional evaluation.
Reputable Organizations Offering Depression Support and Resources
Several organizations offer valuable resources and support for individuals experiencing depression, particularly those with diabetes. These organizations provide a range of services, including helplines, online resources, support groups, and referrals to mental health professionals. Examples include the American Diabetes Association (ADA), which offers educational materials and resources on managing diabetes-related mental health concerns, and the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), a leading source of information and research on mental health disorders, including depression.
The Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance (DBSA) also provides support groups and educational materials for individuals and their families. Local mental health organizations and community centers can also provide valuable resources and referrals.
The Importance of Seeking Professional Help for Depression
While support groups and online resources can be helpful, seeking professional help is crucial for effective treatment of depression. A mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist, psychologist, or therapist, can provide a proper diagnosis, develop a personalized treatment plan, and monitor progress. Professional help ensures access to evidence-based treatments and personalized support, leading to improved mental and physical well-being.
Ignoring depression can lead to worsening symptoms, impacting diabetes management and overall health.
Types of Therapy Effective in Treating Depression
Several types of therapy have proven effective in treating depression. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to depression. CBT is often used in conjunction with diabetes self-management education to improve overall well-being. Other effective therapies include interpersonal therapy, which focuses on improving relationships and communication skills, and psychodynamic therapy, which explores unconscious patterns and conflicts contributing to emotional distress.
Medication, such as antidepressants, may also be prescribed by a psychiatrist or other qualified medical professional to manage symptoms. The choice of therapy depends on individual needs and preferences, and a mental health professional can help determine the most appropriate approach.
Mindfulness Practices for Diabetes Management
Mindfulness, the practice of paying attention to the present moment without judgment, offers a powerful tool for managing diabetes. By cultivating awareness of bodily sensations, thoughts, and emotions, individuals can develop a greater understanding of their responses to stress and improve their ability to regulate blood sugar levels. This approach complements traditional diabetes management strategies, fostering a more holistic and sustainable approach to well-being.Mindfulness techniques can positively influence blood sugar control by reducing stress hormones like cortisol, which can significantly impact blood glucose levels.
When stressed, the body releases cortisol, leading to increased blood sugar. Mindfulness practices help to mitigate the physiological effects of stress, promoting a calmer state and potentially contributing to better blood sugar regulation. Furthermore, mindfulness encourages healthier lifestyle choices, such as mindful eating and increased physical activity, which are crucial components of diabetes management.
Guided Meditation Scripts for Stress Reduction and Improved Self-Awareness
Guided meditations provide a structured approach to cultivating mindfulness. Regular practice can reduce stress, improve self-awareness, and promote emotional regulation – all vital for managing the challenges of living with diabetes. Below are examples of short guided meditations focusing on stress reduction and self-awareness.
Stress Reduction Meditation: Find a comfortable position. Close your eyes gently. Bring your attention to your breath, noticing the sensation of the air entering and leaving your body. If your mind wanders, gently guide it back to your breath. Repeat the phrase “I am calm” silently to yourself with each exhale.
Continue for 5-10 minutes.
Self-Awareness Meditation: Sit comfortably, eyes closed. Bring your attention to your body. Notice any sensations – tingling, warmth, tension. Acknowledge these sensations without judgment. Now, turn your attention to your thoughts and emotions.
Observe them as they arise and pass, like clouds in the sky. Spend 5-10 minutes simply observing without trying to change anything.
Benefits of Incorporating Mindfulness into Daily Routines
Incorporating mindfulness into daily life offers numerous benefits for individuals managing diabetes. These benefits extend beyond blood sugar control, contributing to overall well-being and improved quality of life.The consistent practice of mindfulness can lead to reduced stress and anxiety, improved sleep quality, increased self-compassion, and enhanced emotional regulation. These positive effects contribute to better adherence to diabetes management plans, fostering a more positive and empowered approach to living with the condition.
For example, mindful eating can help prevent impulsive food choices, leading to better blood sugar control.
Step-by-Step Guide to Establishing a Daily Mindfulness Practice
Establishing a daily mindfulness practice requires commitment and consistency, but even short, regular sessions can yield significant benefits.
- Choose a quiet space: Find a comfortable and peaceful environment where you can relax without distractions.
- Set a timer: Start with 5-10 minutes and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable.
- Focus on your breath: Bring your attention to your breath, noticing the sensation of the air entering and leaving your body.
- Acknowledge distractions: When your mind wanders, gently guide it back to your breath without judgment.
- Practice regularly: Aim for daily practice, even if it’s just for a few minutes. Consistency is key.
- Be patient and kind to yourself: Mindfulness is a skill that takes time and practice. Don’t get discouraged if your mind wanders; simply return your attention to your breath.
Mental Health Advocacy and Diabetes
Living with diabetes presents significant challenges, and often, these extend beyond managing blood sugar levels. The emotional toll of chronic illness, coupled with the societal stigma surrounding mental health, can significantly impact a person’s overall well-being and their ability to effectively manage their diabetes. Advocating for better mental health support for individuals with diabetes is crucial for improving their quality of life and health outcomes.The interconnectedness of physical and mental health in diabetes is undeniable.
Untreated anxiety and depression can lead to poor self-care, increased risk of complications, and reduced life expectancy. Conversely, effective management of mental health conditions can empower individuals to actively participate in their diabetes care, leading to improved glycemic control and overall health.
The Impact of Stigma on Mental Health and Diabetes Management
The stigma surrounding mental health conditions creates significant barriers to seeking and receiving appropriate care. Many individuals with diabetes hesitate to disclose their mental health struggles for fear of judgment, discrimination, or perceived weakness. This silence perpetuates a cycle of suffering and prevents individuals from accessing the support they need. This stigma can manifest in various ways, from subtle biases in healthcare settings to overt discrimination in employment and social interactions.
The consequences can be devastating, leading to delayed diagnosis, inadequate treatment, and ultimately, poorer health outcomes. For example, a person might avoid attending support groups or seeking therapy because of fear of being judged negatively by their peers or healthcare providers. This avoidance can worsen feelings of isolation and increase the risk of complications.
Strategies for Effective Advocacy within Communities
Effective advocacy requires a multi-pronged approach involving education, awareness campaigns, and policy changes. Sharing personal stories can be incredibly powerful in breaking down stigma and fostering empathy. Collaborating with diabetes organizations and mental health advocacy groups can amplify the message and reach a wider audience. Engaging in community outreach programs, such as workshops and educational seminars, can provide vital information and resources to those affected.
Advocating for policy changes that ensure equitable access to mental healthcare services is also crucial. This could include advocating for insurance coverage of mental health services, increased funding for research, and the integration of mental health care into diabetes management programs.
Accessing and Utilizing Available Mental Health Services
Numerous resources are available to support individuals with diabetes who are struggling with their mental health. These include individual therapy, group therapy, support groups specifically for people with diabetes, and online resources offering peer support and educational materials. Many primary care physicians are equipped to screen for mental health conditions and provide referrals to specialists. Moreover, several national and international organizations offer helplines, online chat services, and mental health resources tailored to the needs of individuals with diabetes.
It’s crucial to remember that seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness, and that effective mental health support can significantly improve diabetes management and overall well-being. Finding the right therapist or support group may require some trial and error, but persistence is key to finding the support that works best for each individual.
Therapy and Counseling Options for Diabetics: Preventing Diabetic Complications
Living with diabetes can present significant emotional and psychological challenges. The constant monitoring, dietary restrictions, and potential for complications can lead to stress, anxiety, and even depression. Fortunately, various therapy and counseling options can provide invaluable support in managing these challenges and improving overall well-being. These approaches can help individuals develop effective coping mechanisms, enhance self-management skills, and foster a more positive relationship with their condition.
Types of Therapy for Diabetes-Related Stress and Anxiety
Different therapeutic approaches offer unique benefits in addressing the emotional burden of diabetes. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely used method that helps individuals identify and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to stress and anxiety. For example, a person might learn to challenge the thought “One slip-up ruins everything,” replacing it with a more realistic and balanced perspective.
Another effective approach is Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), which focuses on accepting difficult emotions rather than fighting them, while committing to valued actions. This approach can be particularly helpful in navigating the unpredictable nature of blood sugar levels. Finally, mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help individuals manage stress in the moment and cultivate a greater sense of calm and self-awareness.
While CBT focuses on changing thoughts and behaviors, ACT emphasizes acceptance and commitment to values, and MBSR centers on cultivating present moment awareness and stress reduction techniques.
The Role of a Therapist in Supporting Diabetes Self-Management
A therapist plays a crucial role in supporting diabetes self-management by providing a safe and supportive space for individuals to process their emotions, develop coping strategies, and enhance their self-care practices. Therapists can help individuals set realistic goals, improve adherence to treatment plans, and address any psychological barriers to self-management. They can also help patients navigate difficult conversations with family and friends about their diabetes, and advocate for their needs within their healthcare team.
For instance, a therapist might help a patient struggling with adherence to their medication regimen identify underlying anxieties about medication side effects, and develop strategies to address those concerns.
Finding a Qualified Mental Health Professional
Finding a qualified mental health professional is a crucial step in accessing effective support. Several resources can assist in this process. Primary care physicians often have referrals to therapists and counselors specializing in diabetes care. Online directories, such as those maintained by professional organizations like the American Psychological Association or the National Association of Social Workers, allow you to search for practitioners in your area, filtering by specialty and insurance coverage.
It is essential to check the professional’s credentials and experience working with individuals with diabetes. Consider scheduling brief introductory calls with a few different professionals before making a decision to ensure a good fit. A strong therapeutic alliance, built on trust and mutual respect, is vital for successful treatment.
Benefits of Group Therapy for People with Diabetes
Group therapy provides a unique opportunity for individuals with diabetes to connect with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences, learning from each other, and receiving mutual support can significantly reduce feelings of isolation and improve overall well-being. Group therapy settings offer a sense of community and shared understanding that can be particularly helpful in managing the emotional aspects of diabetes.
The group dynamic allows for the exploration of common challenges, such as managing diet, dealing with emotional responses to blood sugar fluctuations, and communicating effectively with healthcare providers. Moreover, group therapy often provides a platform for learning practical coping mechanisms and self-management strategies from both the therapist and other group members.
Building Resilience in Diabetes Management
Living with diabetes presents ongoing challenges, requiring consistent effort and adaptation. Building resilience is not about avoiding difficulties, but rather developing the capacity to cope effectively with them, bounce back from setbacks, and maintain a positive outlook despite the complexities of the condition. This involves cultivating a strong sense of self and employing strategies to manage stress and emotional well-being.Developing resilience is crucial for long-term diabetes management, improving quality of life, and preventing burnout.
A resilient approach allows individuals to view challenges as opportunities for growth, fostering a proactive and optimistic mindset essential for navigating the demands of daily diabetes care. This section will explore key strategies for cultivating resilience and building a supportive environment for managing diabetes effectively.
Strategies for Building Resilience
Resilience isn’t an innate trait; it’s a skill developed over time through conscious effort and practice. Several strategies can significantly enhance an individual’s ability to cope with the daily challenges of diabetes. These strategies focus on building coping mechanisms, fostering self-compassion, and developing problem-solving skills.
- Practice Mindfulness and Meditation: Regular mindfulness exercises can help manage stress and improve emotional regulation, allowing for a more balanced response to diabetes-related challenges. Imagine focusing on your breath, noticing sensations in your body without judgment, and gently redirecting your attention when your mind wanders. This practice cultivates present moment awareness and reduces reactivity to stressful situations.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Exercise not only contributes to better blood sugar control but also acts as a powerful stress reliever and mood booster. Even moderate physical activity, such as a brisk walk, can significantly improve mental and emotional well-being. Consider activities you enjoy, such as swimming, cycling, or dancing, to make exercise a sustainable part of your routine.
- Prioritize Healthy Sleep: Sufficient sleep is essential for both physical and mental health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support your body’s natural restorative processes and enhance your ability to cope with stress. Establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensure a comfortable sleep environment.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels and overall well-being. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Consistent healthy eating contributes to both physical and emotional stability, making it easier to manage diabetes-related stress.
- Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Learning effective problem-solving techniques empowers individuals to address challenges proactively. This involves breaking down problems into smaller, manageable steps, identifying potential solutions, and evaluating their effectiveness. Consider keeping a journal to track challenges and solutions, noting patterns and developing strategies for future similar situations.
Self-Compassion and Self-Acceptance in Diabetes Management
Self-compassion involves treating oneself with the same kindness and understanding one would offer a close friend facing similar challenges. Self-acceptance acknowledges the realities of living with diabetes without self-criticism or judgment. This approach is fundamental to building resilience and maintaining a positive self-image despite the inevitable ups and downs of managing the condition.
“Self-compassion is not self-indulgence; it is self-care.”
Practicing self-compassion involves recognizing that mistakes and setbacks are a normal part of the learning process, and that self-criticism only hinders progress. It’s about acknowledging feelings of frustration or disappointment without letting them overwhelm you. This approach fosters a healthier relationship with oneself and reduces the negative emotional impact of diabetes-related challenges.
Building Emotional Support Networks
Having a strong support system is crucial for managing the emotional and psychological demands of living with diabetes. Connecting with others who understand the challenges can provide invaluable encouragement, practical advice, and emotional support.Building an emotional support network can involve several strategies. This might include joining a diabetes support group, connecting with friends and family, or seeking professional support from a therapist or counselor.
Open communication with loved ones about the challenges of diabetes is essential to building understanding and support. Sharing experiences and seeking advice from others can significantly improve one’s coping mechanisms and overall well-being.
Sleep and Mental Health in Diabetes
Managing diabetes effectively requires a holistic approach, encompassing not only blood sugar control but also mental and emotional well-being. A crucial, often overlooked, component of this holistic approach is sleep. The intricate connection between sleep quality, mental health, and diabetes management significantly impacts overall health outcomes. Insufficient or poor-quality sleep can exacerbate existing diabetes complications and negatively influence mental health, creating a vicious cycle that hinders effective diabetes management.Sleep quality significantly influences blood sugar regulation and emotional stability.
Studies have shown a strong correlation between sleep deprivation and impaired glucose tolerance, leading to higher blood sugar levels. Furthermore, lack of sleep can amplify feelings of stress, anxiety, and depression, all of which are known to negatively affect diabetes management and increase the risk of complications. Conversely, adequate sleep promotes better emotional regulation, reduces stress hormones, and contributes to improved self-management capabilities for individuals with diabetes.
The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Blood Sugar Control and Emotional Well-being
Sleep deprivation directly affects the body’s hormonal balance, impacting insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. When sleep is insufficient, the body releases higher levels of cortisol and other stress hormones, which counter the effects of insulin, leading to increased blood glucose levels. This disruption in hormonal regulation contributes to poor blood sugar control and increased risk of long-term complications. Concurrently, lack of sleep exacerbates emotional vulnerability, increasing irritability, mood swings, and feelings of anxiety and depression.
These emotional challenges can significantly hinder adherence to diabetes management plans, further impacting blood sugar control. For example, a person consistently experiencing sleep deprivation might find it more difficult to stick to their prescribed diet and exercise regimen, leading to uncontrolled blood sugar levels and increased risk of complications.
Improving Sleep Hygiene and Promoting Better Sleep Patterns
Establishing good sleep hygiene is crucial for improving sleep quality and promoting better sleep patterns. This involves creating a consistent sleep schedule, maintaining a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing the sleep environment. A consistent sleep schedule helps regulate the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, improving sleep quality and reducing daytime sleepiness. A relaxing bedtime routine might include taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music, helping to wind down before bed.
Optimizing the sleep environment involves ensuring a dark, quiet, and cool room, promoting restful sleep. For example, using blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine can help create a conducive environment for sleep. Additionally, limiting screen time before bed and avoiding caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime can further improve sleep quality.
The Relationship Between Sleep Disorders and Diabetes Complications
Sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea and insomnia, are strongly associated with an increased risk of diabetes complications. Sleep apnea, characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, can lead to oxidative stress and inflammation, contributing to the development and progression of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy. Insomnia, a condition characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, can also negatively impact blood sugar control and exacerbate existing mental health challenges, increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
For instance, individuals with untreated sleep apnea may experience significantly higher rates of cardiovascular events and poorer glycemic control compared to those without the disorder. Addressing sleep disorders through appropriate interventions, such as CPAP therapy for sleep apnea or cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia, can significantly improve diabetes management and reduce the risk of complications.
Successfully preventing diabetic complications requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses diligent self-management, proactive healthcare, and a strong support system. By understanding the risks, adopting healthy habits, and seeking appropriate medical guidance, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their chances of developing serious complications. This guide serves as a starting point on a journey towards better health and well-being, emphasizing the importance of proactive management and the transformative power of self-care.
FAQ Guide
What are the early warning signs of diabetic neuropathy?
Early signs of diabetic neuropathy can include numbness, tingling, burning, or pain in the hands and feet. These sensations may be mild at first and gradually worsen.
Can diabetes be reversed?
While a complete reversal of type 2 diabetes is possible in some cases through significant lifestyle changes and weight loss, it’s not always achievable. However, achieving remission is often a realistic goal, significantly reducing the need for medication and improving overall health.
How often should I see my doctor for diabetes management?
The frequency of doctor visits for diabetes management varies depending on individual needs and the severity of the condition. Regular check-ups, including blood tests and examinations, are crucial for monitoring blood sugar levels and overall health.
What are the best types of exercise for managing diabetes?
Regular aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, is highly beneficial for managing blood sugar levels. Strength training is also important for maintaining muscle mass and overall health.





